react源码学习之mapChildren
/ / 点击 / 阅读耗时 8 分钟基于16.12.0。
我们都知道children是react元素对象的一个属性,用来承载一个父组件所有包含的子组件。react官方推出了一套api用来处理children对象,这篇就是用来记录学习react对map函数的实现。
流程
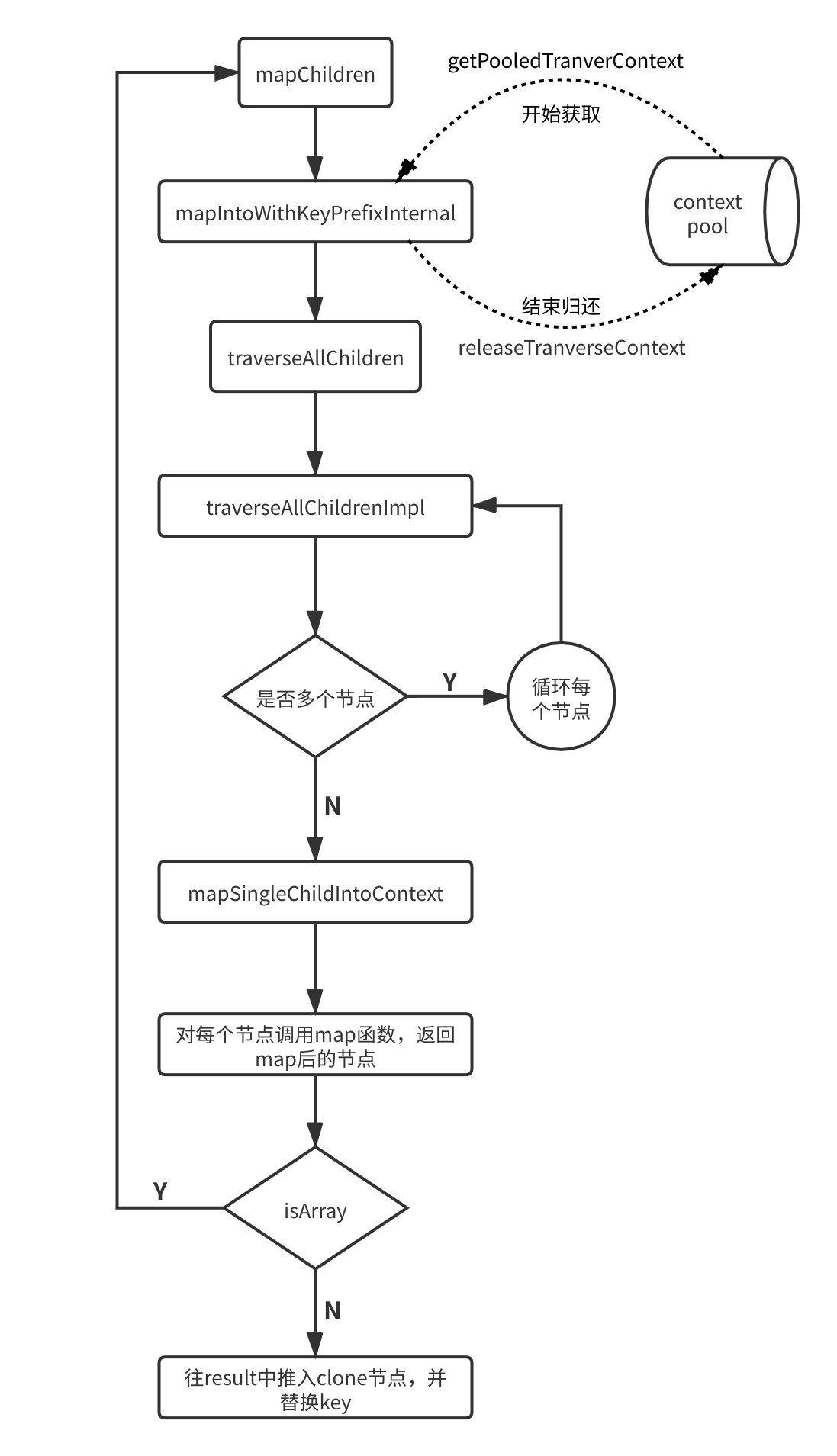
(参考自慕课网教程)
函数分析
mapChildren
好像没啥好写的。。。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8function mapChildren(children, func, context) {
if (children == null) {
return children;
}
const result = [];
mapIntoWithKeyPrefixInternal(children, result, null, func, context);
return result;
}mapIntoWithKeyPrefixInternal
第一步是从对象池中获取一个包含特定属性的对象,这个对象可以认为是处理同一级各个child的一个环境对象;
第二步是利用这个环境对象做具体的child的遍历处理;
第三步是释放这个对象,如果对象池中已经有10个了,就彻底释放,如果不到10个就存入对象池。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14function mapIntoWithKeyPrefixInternal(children, array, prefix, func, context) {
let escapedPrefix = '';
if (prefix != null) {
escapedPrefix = escapeUserProvidedKey(prefix) + '/';
}
const traverseContext = getPooledTraverseContext(
array,
escapedPrefix,
func,
context,
);
traverseAllChildren(children, mapSingleChildIntoContext, traverseContext);
releaseTraverseContext(traverseContext);
}之所以使用对象池,是因为map在执行的过程中,会涉及声明大量对象及再释放,这些操作是一个消耗性能的过程,可能会导致js引擎积塞,引发内存抖动。
getPooledTraverseContext和releaseTraverseContext
一个特定traverseContext对象的发挥作用的阶段对应处理同一层级的所有child的过程。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37const POOL_SIZE = 10;
const traverseContextPool = [];
function getPooledTraverseContext(
mapResult,
keyPrefix,
mapFunction,
mapContext,
) {
if (traverseContextPool.length) {
const traverseContext = traverseContextPool.pop();
traverseContext.result = mapResult;
traverseContext.keyPrefix = keyPrefix;
traverseContext.func = mapFunction;
traverseContext.context = mapContext;
traverseContext.count = 0;
return traverseContext;
} else {
return {
result: mapResult,
keyPrefix: keyPrefix,
func: mapFunction,
context: mapContext,
count: 0,
};
}
}
function releaseTraverseContext(traverseContext) {
traverseContext.result = null;
traverseContext.keyPrefix = null;
traverseContext.func = null;
traverseContext.context = null;
traverseContext.count = 0;
if (traverseContextPool.length < POOL_SIZE) {
traverseContextPool.push(traverseContext);
}
}traverseAllChildren
这个函数会返回处理了的同一层级的child的数量。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7function traverseAllChildren(children, callback, traverseContext) {
if (children == null) {
return 0;
}
return traverseAllChildrenImpl(children, '', callback, traverseContext);
}traverseAllChildrenImpl
这段函数里有一个递归的过程,对应流程图中的那个小环。整个children的处理过程都使用同一个traverseContext对象。
元素的key属性也是在这个函数中计算得出。
可以看出能处理的类型包含:普通字符串、数字、虚拟dom对象、迭代器、前面说的这些类型组成的数组。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92function traverseAllChildrenImpl(
children,
nameSoFar,
callback,
traverseContext,
) {
const type = typeof children;
if (type === 'undefined' || type === 'boolean') {
// All of the above are perceived as null.
children = null;
}
let invokeCallback = false;
if (children === null) {
invokeCallback = true;
} else {
switch (type) {
case 'string':
case 'number':
invokeCallback = true;
break;
case 'object':
switch (children.$$typeof) {
case REACT_ELEMENT_TYPE:
case REACT_PORTAL_TYPE:
invokeCallback = true;
}
}
}
if (invokeCallback) {
callback(
traverseContext,
children,
// If it's the only child, treat the name as if it was wrapped in an array
// so that it's consistent if the number of children grows.
nameSoFar === '' ? SEPARATOR + getComponentKey(children, 0) : nameSoFar,
);
return 1;
}
let child;
let nextName;
let subtreeCount = 0; // Count of children found in the current subtree.
const nextNamePrefix =
nameSoFar === '' ? SEPARATOR : nameSoFar + SUBSEPARATOR;
if (Array.isArray(children)) {
for (let i = 0; i < children.length; i++) {
child = children[i];
nextName = nextNamePrefix + getComponentKey(child, i);
subtreeCount += traverseAllChildrenImpl(
child,
nextName,
callback,
traverseContext,
);
}
} else {
const iteratorFn = getIteratorFn(children);
if (typeof iteratorFn === 'function') {
const iterator = iteratorFn.call(children);
let step;
let ii = 0;
while (!(step = iterator.next()).done) {
child = step.value;
nextName = nextNamePrefix + getComponentKey(child, ii++);
subtreeCount += traverseAllChildrenImpl(
child,
nextName,
callback,
traverseContext,
);
}
} else if (type === 'object') {
let addendum = '';
const childrenString = '' + children;
invariant(
false,
'Objects are not valid as a React child (found: %s).%s',
childrenString === '[object Object]'
? 'object with keys {' + Object.keys(children).join(', ') + '}'
: childrenString,
addendum,
);
}
}
return subtreeCount;
}mapSingleChildIntoContext
首先判断经过使用者传入函数的处理后返回的是不是一个数组,如果是,则递归mapIntoWithKeyPrefixInternal,重复上述过程,对应流程图中的大环;
如果是单个元素,则将上一步生成的key和这一步计算后得到的child一同传入ReactElement函数中,返回一个普通的虚拟dom元素,推入结果池中。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22function mapSingleChildIntoContext(bookKeeping, child, childKey) {
const {result, keyPrefix, func, context} = bookKeeping;
let mappedChild = func.call(context, child, bookKeeping.count++);
if (Array.isArray(mappedChild)) {
mapIntoWithKeyPrefixInternal(mappedChild, result, childKey, c => c);
} else if (mappedChild != null) {
if (isValidElement(mappedChild)) {
mappedChild = cloneAndReplaceKey(
mappedChild,
// Keep both the (mapped) and old keys if they differ, just as
// traverseAllChildren used to do for objects as children
keyPrefix +
(mappedChild.key && (!child || child.key !== mappedChild.key)
? escapeUserProvidedKey(mappedChild.key) + '/'
: '') +
childKey,
);
}
result.push(mappedChild);
}
}
函数所在文件路径